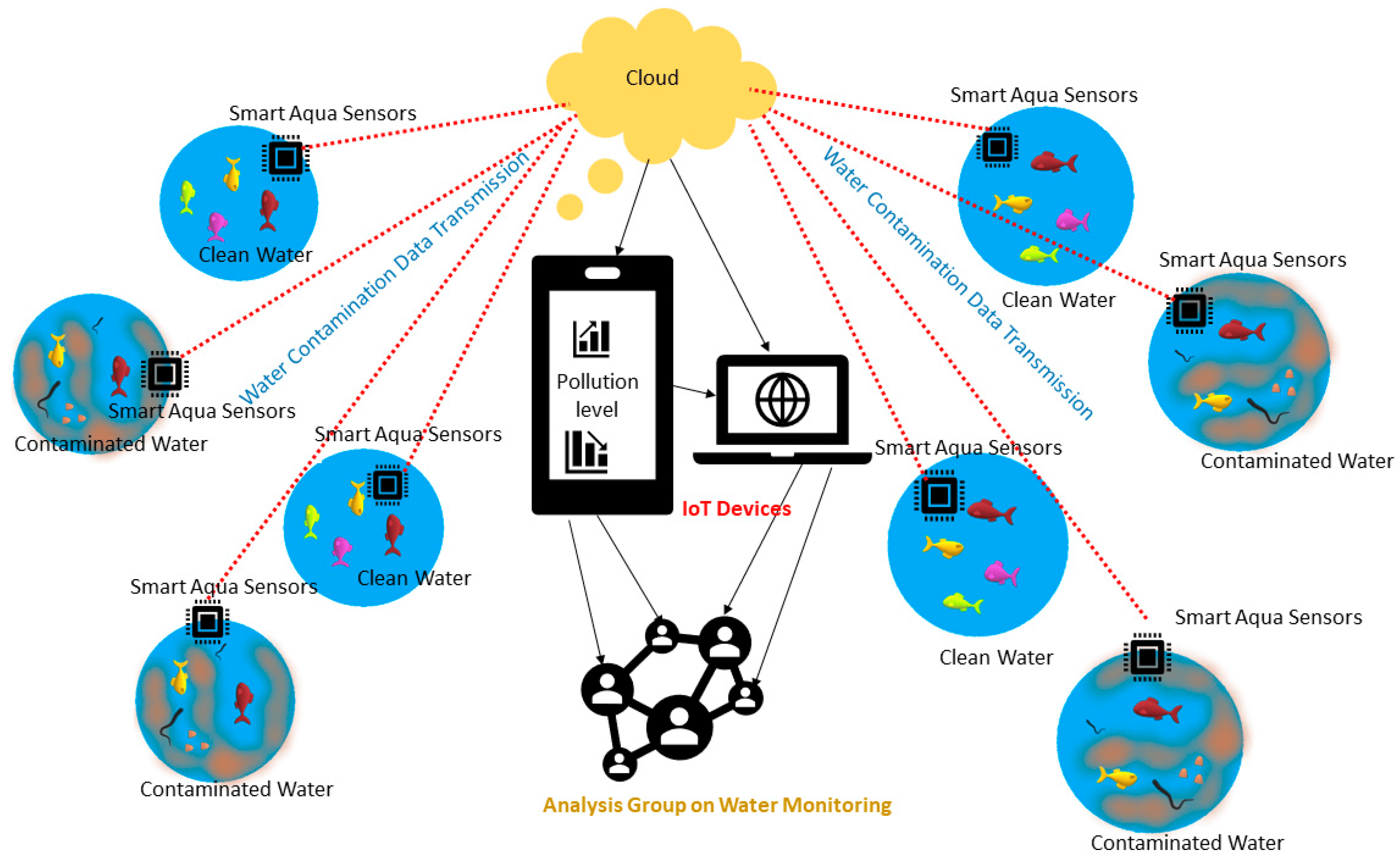
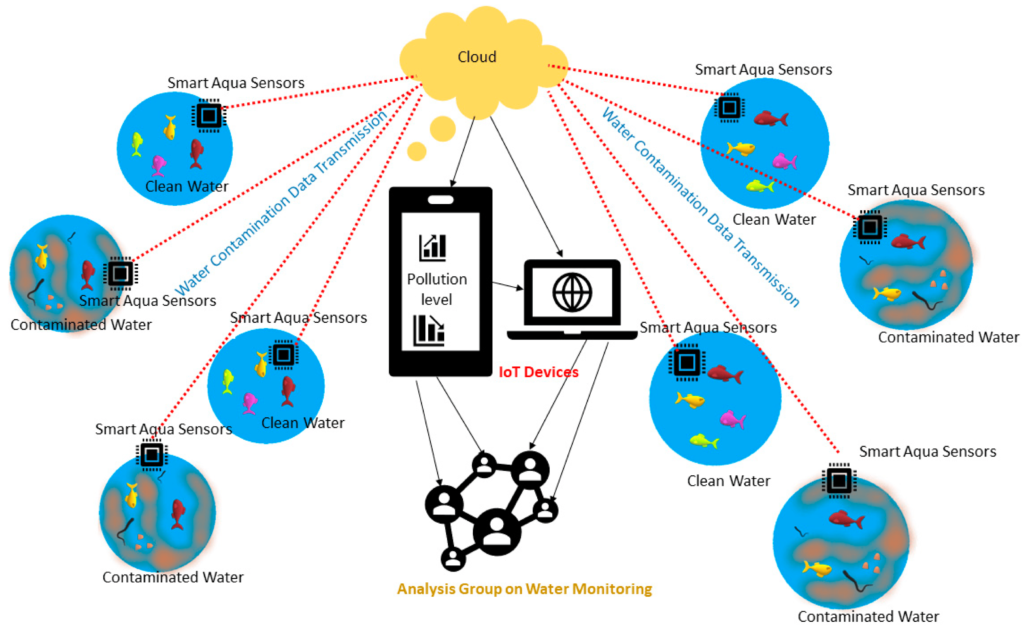
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing how devices, objects, and systems connect and interact, ushering in an era of smart environments. From homes and cities to industries and healthcare, IoT enables seamless communication between physical devices and the digital world, unlocking new possibilities for efficiency, automation, and convenience.
Understanding IoT
IoT refers to the network of interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect and exchange data over the internet. These devices can range from everyday objects such as smart thermostats and wearable fitness trackers to complex machinery used in industrial settings.
Key Components of IoT
- Sensors and Connectivity: IoT devices are equipped with sensors to capture real-time data from their environment. Connectivity options include Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks, enabling devices to transmit data to centralized systems or other connected devices.
- Data Processing and Analytics: Collected data undergoes processing and analysis using cloud computing or edge computing platforms. Advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning algorithms, help derive actionable insights from the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices.
- Automation and Control: IoT enables automation of tasks and processes based on data-driven insights. For example, smart home devices can adjust lighting and temperature settings based on occupancy and preferences, while industrial IoT systems can optimize manufacturing processes in real time.
Applications of IoT

IoT is transforming various sectors and industries:
- Smart Homes: IoT devices like smart speakers, lighting systems, and security cameras enhance home automation and energy efficiency.
- Smart Cities: IoT technologies monitor and manage urban infrastructure, improving traffic management, waste management, and public safety.
- Healthcare: IoT-enabled medical devices enable remote patient monitoring, personalized treatment plans, and efficient healthcare delivery.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): IoT enhances operational efficiency in manufacturing by enabling predictive maintenance, inventory management, and supply chain optimization.
Challenges and Considerations
While IoT offers immense benefits, several challenges must be addressed:
- Security and Privacy: Protecting IoT devices from cyber threats and ensuring data privacy are critical concerns.
- Interoperability: IoT devices often come from different manufacturers, requiring standards and protocols for seamless integration and communication.
- Scalability: Managing large-scale IoT deployments and handling massive amounts of data pose scalability challenges.
Future Trends
The future of IoT holds promising developments:
- 5G Connectivity: Faster and more reliable 5G networks will support the proliferation of IoT devices and applications.
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to the source (at the edge) reduces latency and bandwidth usage, enhancing IoT efficiency.
- AI and Machine Learning: Integration of AI and machine learning algorithms will enable IoT devices to autonomously learn and adapt based on data patterns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IoT is reshaping our world by creating interconnected ecosystems that enhance efficiency, productivity, and quality of life. As IoT technologies continue to evolve and become more integrated into daily life and industry, businesses and consumers alike stand to benefit from smarter, more connected environments. Embracing IoT requires addressing challenges such as security and interoperability while leveraging advancements in connectivity and data analytics to unlock the full potential of this transformative technology.