Internet connectivity plays a pivotal role in shaping global access to information, education, economic opportunities, and social services. However, disparities in internet access—referred to as the digital divide—persist globally, impacting individuals, communities, and economies differently. Bridging this divide is crucial for achieving digital inclusion and harnessing the full potential of the digital age.

Understanding the Digital Divide
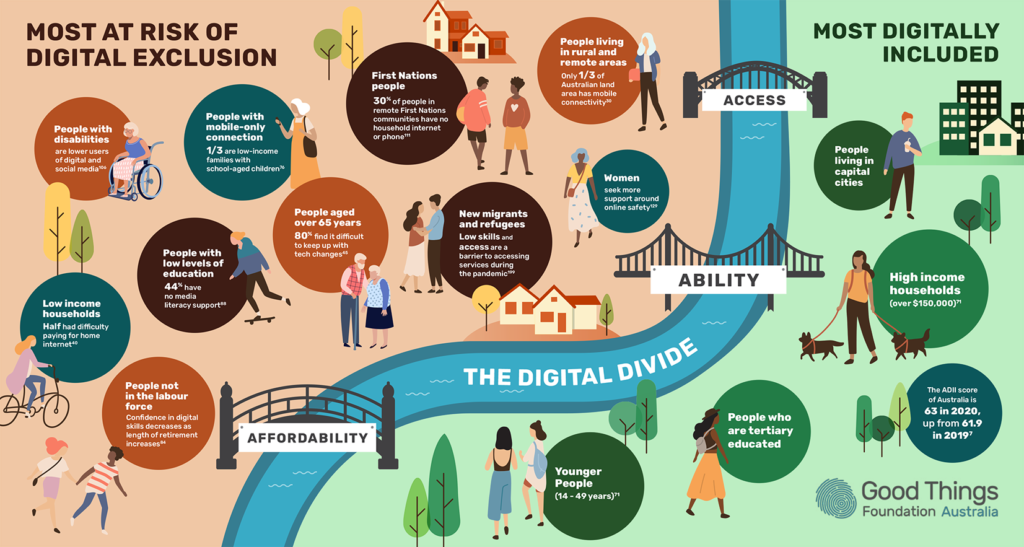
The digital divide encompasses inequalities in access to and use of information and communication technologies (ICTs), particularly internet services. Factors contributing to the digital divide include:
- Infrastructure: Disparities in broadband infrastructure and coverage between urban and rural areas, as well as within low-income and marginalized communities.
- Affordability: High costs associated with internet services, devices, and data plans, limiting accessibility for individuals with limited financial resources.
- Digital Literacy: Variations in digital skills and literacy levels among different demographic groups, affecting their ability to effectively utilize online resources and services.
Impact of Internet Connectivity
- Education: Internet access enhances educational opportunities by providing students with resources for research, online learning platforms, and access to digital libraries. Bridging the digital divide in education promotes lifelong learning and skills development essential for the knowledge economy.
- Economic Development: Access to the internet fosters entrepreneurship, e-commerce, and digital innovation, enabling small businesses and startups to reach global markets and participate in the digital economy. It also facilitates remote work opportunities and job creation, particularly in underserved regions.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine and digital health services rely on internet connectivity to deliver remote consultations, medical information, and patient monitoring, enhancing healthcare access in rural and remote areas where physical healthcare facilities are scarce.
- Social Inclusion: Internet access promotes social inclusion by connecting individuals to social networks, support communities, and government services. It facilitates communication among geographically dispersed families and friends, reducing social isolation.
Initiatives and Solutions
Governments, international organizations, and private sector stakeholders are implementing initiatives to bridge the digital divide:
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in broadband infrastructure expansion and digital connectivity projects in underserved areas to improve internet access and reliability.
- Affordability Programs: Subsidies, tax incentives, and partnerships to reduce the cost of internet services, devices, and data plans for low-income households and marginalized communities.
- Digital Skills Training: Programs promoting digital literacy, skills development, and training initiatives to empower individuals with the knowledge to navigate and utilize digital technologies effectively.
Challenges and Considerations
- Socioeconomic Factors: Economic disparities and income inequality influence individuals’ ability to afford and access internet services, exacerbating the digital divide.
- Infrastructure Limitations: Remote and rural areas face challenges in infrastructure deployment due to geographical barriers, high costs, and technical feasibility.
- Regulatory Policies: Regulatory frameworks, spectrum allocation, and licensing requirements impact internet service providers’ ability to expand coverage and invest in infrastructure development.
Future Outlook
The future of internet connectivity lies in collaborative efforts to address infrastructure gaps, enhance affordability, and promote digital literacy worldwide. Emerging technologies such as satellite internet, 5G networks, and community networks hold promise in extending connectivity to underserved populations and bridging the digital divide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, internet connectivity is essential for fostering inclusive socioeconomic development, promoting digital inclusion, and bridging the digital divide globally. By expanding access to reliable, affordable internet services and enhancing digital literacy, societies can leverage the transformative power of digital technologies to empower individuals, communities, and economies. Embracing collaborative strategies, innovative solutions, and inclusive policies will be instrumental in achieving universal internet access and realizing the full potential of a connected world.