Robotics and automation technologies have revolutionized industries, from traditional manufacturing processes to advanced healthcare applications, by enhancing efficiency, precision, and scalability. These technologies leverage artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and mechanical engineering to automate tasks traditionally performed by humans, offering transformative solutions that improve productivity, quality, and safety across diverse sectors.
Understanding Robotics and Automation
Robotics refers to the design, construction, and use of robots to perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously. Automation encompasses the use of technology and control systems to streamline operations, reduce human intervention, and optimize processes for efficiency and reliability.
Applications in Manufacturing
- Industrial Robots: Automated robotic arms and machines perform repetitive tasks such as assembly, welding, and material handling in manufacturing plants. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside human workers to enhance productivity and flexibility on production lines.
- Quality Control: Automated systems use sensors and AI algorithms for real-time inspection, defect detection, and quality assurance in manufacturing processes, ensuring consistent product quality and reducing waste.
- Inventory Management: Robotics and automation streamline inventory tracking, warehouse operations, and supply chain logistics with autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic systems that optimize storage and retrieval tasks.
Applications in Healthcare
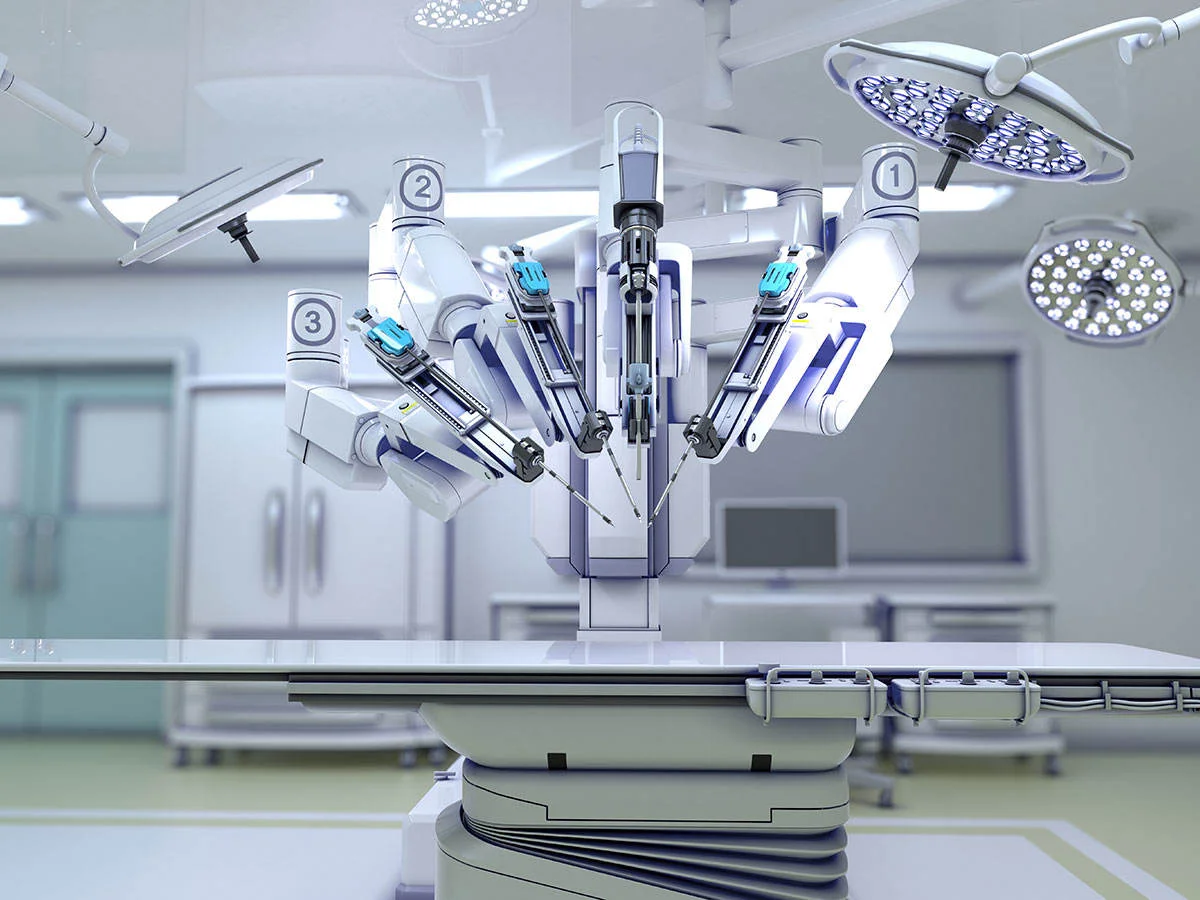
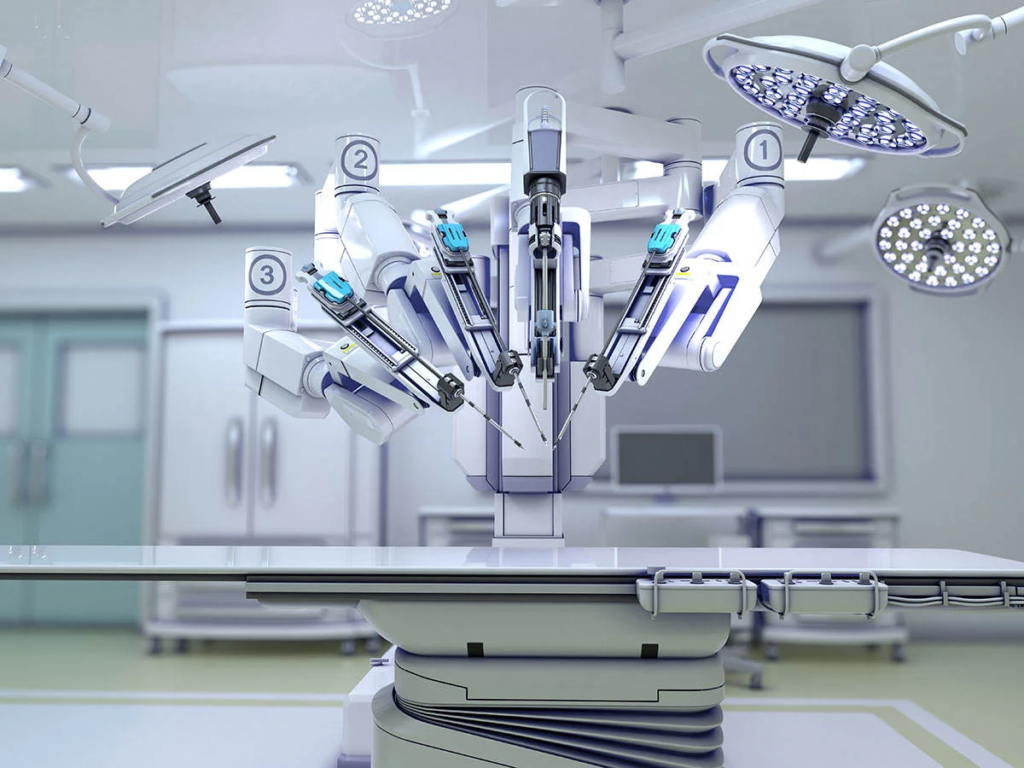
- Surgical Robotics: Robotic-assisted surgery enhances precision, minimizes invasiveness, and improves surgical outcomes for procedures ranging from orthopedics to neurosurgery. Surgeons control robotic arms equipped with cameras and surgical tools to perform delicate procedures with enhanced dexterity and accuracy.
- Telemedicine and Patient Care: Robotics and automation support telemedicine platforms with remote monitoring devices, telepresence robots, and AI-driven diagnostics that enhance patient monitoring, personalized care, and medical consultations.
- Rehabilitation and Assistance: Robotic exoskeletons and assistive devices aid in physical rehabilitation, mobility assistance, and support for individuals with disabilities, improving independence and quality of life.
Benefits of Robotics and Automation

Implementing robotics and automation offers several benefits across industries:
- Improved Efficiency: Automation streamlines processes, reduces cycle times, and increases production output with minimal errors or downtime, enhancing operational efficiency and competitiveness.
- Enhanced Safety: Robots perform hazardous tasks, such as handling toxic chemicals or working in extreme environments, reducing workplace accidents and protecting human workers from potential risks.
- Precision and Quality: Robotics ensure consistent product quality, precise measurements, and adherence to strict manufacturing tolerances, enhancing overall product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its advantages, robotics and automation face challenges:
- Cost and Investment: Initial capital investment in robotics systems, maintenance costs, and workforce training require substantial financial resources for adoption and integration.
- Technological Integration: Integrating robotics with existing infrastructure, ensuring compatibility with legacy systems, and overcoming technical barriers like sensor accuracy and reliability are critical considerations.
- Ethical and Employment Implications: Addressing concerns about job displacement, workforce reskilling, and ethical considerations surrounding AI and autonomous systems in healthcare and other sensitive sectors.
Future Outlook
The future of robotics and automation is promising with advancements in AI, machine learning, and robotics technologies. Emerging trends such as autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), AI-driven decision-making, and human-robot collaboration (HRC) will drive innovation across industries and expand the scope of applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, robotics and automation technologies have transformed manufacturing processes, healthcare delivery, and various industries by enhancing efficiency, precision, and safety. By leveraging AI, machine learning, and robotic systems, organizations optimize operations, improve productivity, and drive innovation in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Embracing robotics and automation requires strategic planning, investment in technology, and collaborative efforts to harness their full potential in enhancing competitiveness and advancing societal well-being globally.